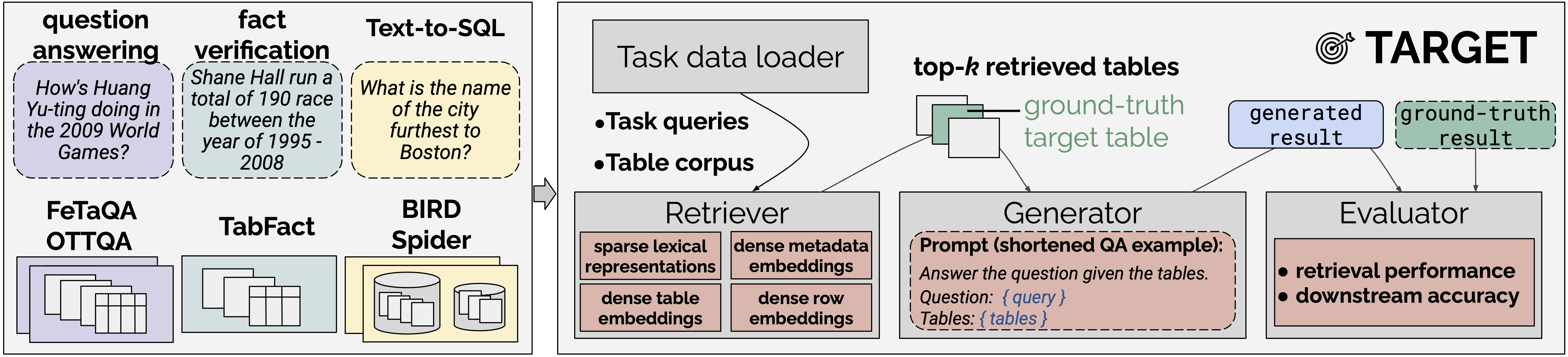
The data landscape is rich with structured data, often of high value to organizations, driving important applications in data analysis and machine learning. Recent progress in representation learning and generative models for such data has led to the development of natural language interfaces to structured data, including those leveraging text-to-SQL. Contextualizing interactions, either through conversational interfaces or agentic components, in structured data through retrieval-augmented generation can provide substantial benefits in the form of freshness, accuracy, and comprehensiveness of answers. The key question is: how do we retrieve the right table(s) for the analytical query or task at hand? To this end, we introduce TARGET: a benchmark for evaluating TAble Retrieval for GEnerative Tasks. With TARGET we analyze the retrieval performance of different retrievers in isolation, as well as their impact on downstream tasks. We find that dense embedding-based retrievers far outperform a BM25 baseline which is less effective than it is for retrieval over unstructured text. We also surface the sensitivity of retrievers across various metadata (e.g., missing table titles), and demonstrate a stark variation of retrieval performance across datasets and tasks.
@inproceedings{ji2024target,
title={TARGET: Benchmarking Table Retrieval for Generative Tasks},
author={Ji, Xingyu and Parameswaran, Aditya and Hulsebos, Madelon},
booktitle={NeurIPS 2024 Third Table Representation Learning Workshop}
}